What is solar energy, and how solar energy works, is no longer a mystery; it’s the future of power. One major type of solar energy system uses reflective mirrors to concentrate sunlight. This energy turns it into steam to drive turbines and generate electricity. With rising interest in solar energy in India, understanding solar panels and how they work is more relevant than ever. From powering homes to entire cities, the uses of solar energy are vast.
Harnessing the Power of the Sun: What is Solar Energy?
Here’s a stat that is quite well known at this point (and still pretty hard to wrap our heads around): the energy that hits the surface of the Earth in an hour and a half is sufficient to supply the global energy demand for a year. We are talking about energy for everything, from lighting up our megacities to making food for 8 billion people. Now, imagine if we could build a bucket to capture even a fraction of this solar energy; it would have phenomenal implications for how we run our societies and their economies. And the good news is, we have some tricks to bottle up this light, and we are getting better and better at it.
Solar Concentrators vs Solar Panels: Which One Powers the Future
Solar Concentrators:
This is how solar concentrators, our first kind of light bucket, work as well.
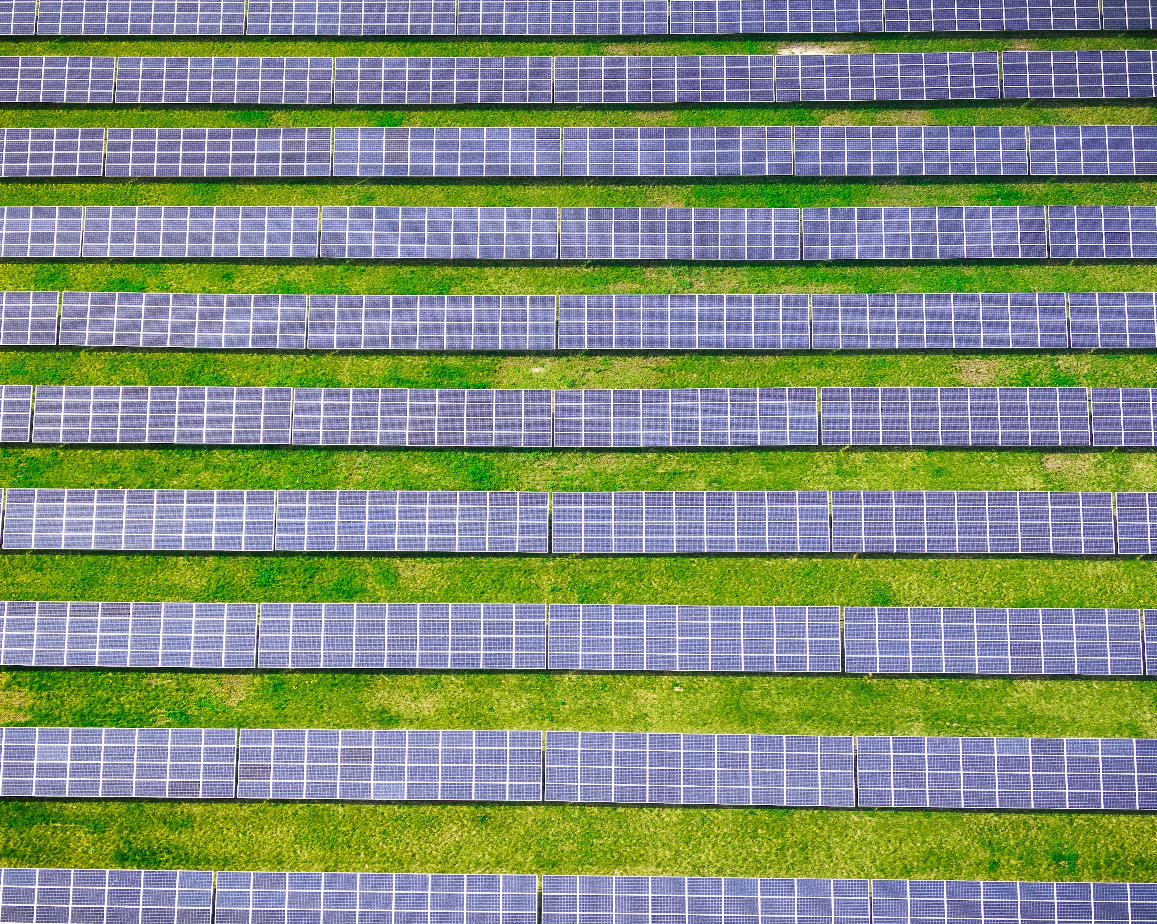
- Solar concentrators are large mirrors that reflect and focus sunlight onto something similar to a water tower.
- The heat turns water into steam, which is directed to turbines, and zap! We get power.
- These concentrator mirrors are spread across acres of land.
- Aerial shots of these farms are often quite a sight to behold.
This is one of the earliest examples of understanding what solar energy is in action, using sunlight to generate electricity through heat and turbines.
Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules):
Our second kind of light bucket is quite special, and yes, we are talking about solar panels (or to be more accurate, photovoltaic modules).
What makes solar panels stand apart from every other energy system so far is that they convert electricity directly.
- No spinning turbines are involved at all; this is a core part of how solar panels work.
- Just find a sunny spot to place them, and on the other end connect wires, and electricity begins to flow. Easy peasy. And this is huge news, because since you don’t need large turbines, instead of building these massive power stations, you can put them anywhere in any form and shape.
- On your roof, in your calculators (and even in space).
- Also, since there aren’t any moving parts, these panels can last for a really long time, often 20 to 25 years.
This makes solar panels a revolutionary answer to the question: What is solar energy, and how can we use solar panels more efficiently?
Explore the Science Behind How Solar Panels Work
When sunlight hits a photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons. If conductors are joined to the positive and negative sides of the cell, the flow of electrons produces an electric current. Many such cells form a solar module, and multiple modules combine to form a solar system. The more panels you add, the more energy you can generate to power larger appliances a great example of what solar energy is in real use.
However, in most cases, you can’t directly connect a solar panel to an appliance; it must pass through an inverter. Here’s why!
DC to AC: The Role of Inverters
Solar panels generate Direct Current (DC) electricity, which flows in one direction. But most buildings use Alternating Current (AC) electricity, the kind that powers our wall sockets. So, to make solar panels usable for everyday needs, the inverter converts DC to AC and sends it to your electrical panel, distributing it throughout the building. This is key to understanding what solar energy is and how solar panels work to power our lives.

Breaking Down Solar Panels and the Types You Should Know
-
Monocrystalline solar panels:
If you see a solar panel with black cells, it’s presumably a monocrystalline panel. These cells appear black thanks to how light interacts with the pure silicon crystal. Being made out of pure silicon ingots, they have the maximum efficiency among all types.
-
Polycrystalline solar panels:
Unlike monocrystalline solar cells, polycrystalline solar cells tend to possess a bluish hue because of the sunshine reflecting off the silicon fragments within the cell in a distinct way.
>Although it is less efficient than the single-crystal cells found in monocrystalline panels and requires more modules to achieve the same performance, polycrystalline panels are cheaper as manufacturing the silicon cells is cheaper, as well as the assembly is cost-effective and easier. Compared to mono, they are more affected by high temperatures and reduce productivity on the hottest days.
-
Thin-film solar panels:
The biggest differentiating factor when it comes to thin-film solar panels is, as their name suggests, how thin and low-profile the technology is. These panels are often slimmer than others. By using cells that are roughly 350 times thinner than the crystalline wafers used in typical solar panels.
Thin-film solar panels are less efficient and have lower power capacity than single crystal and polycrystalline solar cell types.
-
PERC:
It stands for “passivated emitter and rear contact” or “rear cell”. PERC solar panels have an additional layer on the rear of the conventional solar cells that allows more sunlight to be captured and have become electricity. This makes PERC cells more efficient than traditional cells. PERC panels are available in both mono and polycrystalline configurations.
Conclusion:
Solar energy is no longer just an alternative, it’s becoming the foundation of a cleaner, more sustainable future. From large-scale solar concentrators to compact and efficient solar panels, we now have multiple ways to harness the sun’s power. Understanding what is solar energy and how solar panels work helps us make informed choices about powering our homes, businesses, and communities. As technology advances and options like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, and PERC panels become more accessible, solar energy stands as a powerful solution for a brighter tomorrow.</span>